
The remaining two hybrid orbitals form bonds by overlapping with the \(1s\) orbital of a hydrogen atom. ISBN 8-8.\) is explained as follows: one of the three \(sp^2\) hybrids forms a bond by overlapping with the identical hybrid orbital on the other carbon atom. Pyykkö, Pekka Riedel, Sebastian Patzschke, Michael (2005).Comparing Single, Double, and Triple Bonds Nitrogen also forms triple bonds with itself and with carbon.Įxamples of molecules with triple bonds include nitrogen (N 2, N ≡N), carbon monoxide (CO, C ≡O), acetylene (C 2H 2, H-C ≡C-H), and cyanogen (C 2N 2, N ≡C-C ≡N).Ī triple bond consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds. Solution For Each carbon atom in T forms a sigma () bond to at least one other carbon atom, as shown.On the diagram, draw the orbitals that represent the bond that is also present in T Solution For Each carbon atom in T forms a sigma () bond to at least one other carbon atom, as shown. The most common triple bond occurs between two carbon atoms in the alkynes. The symbol for the triple bond is a triple dash, as in N ≡N. Sigma bond ( bond): A covalent bond formed by overlap of atomic orbitals and/or hybrid orbitals along the bond axis (i.e., along a line connected the two. Triple BondĪ triple bond forms when two atoms share three electron pairs. A pi bond forms by sideways overlapping of p orbitals.
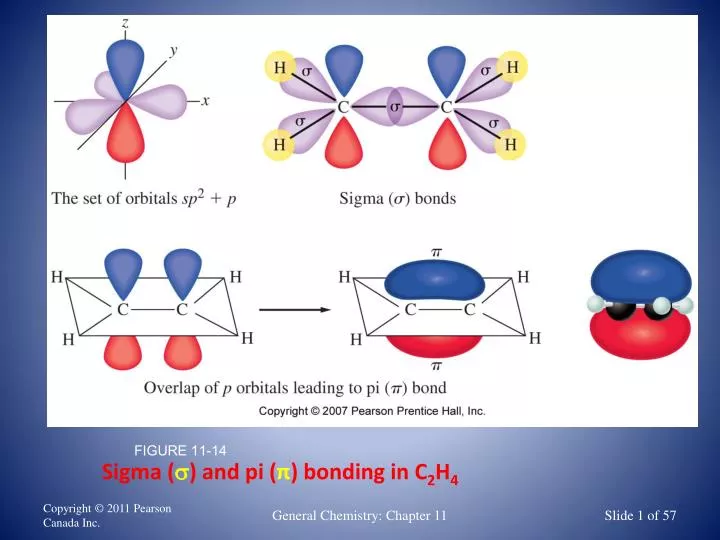
The double bond consists of one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond. Carbon and members of the oxygen family of elements (the chalcogens) participate in double bonds.Įxamples of double bonds are O 2 (oxygen, O=O), CO 2 (carbon dioxide, O=C=O), and C 2H 2 (ethylene, H-C=C-H). The symbol for this is a double dash or equal sign between the two atoms, like O=O. Double BondĪ double bond forms when two atoms share two electron pairs or six electrons.

SIGMA BOND FREE
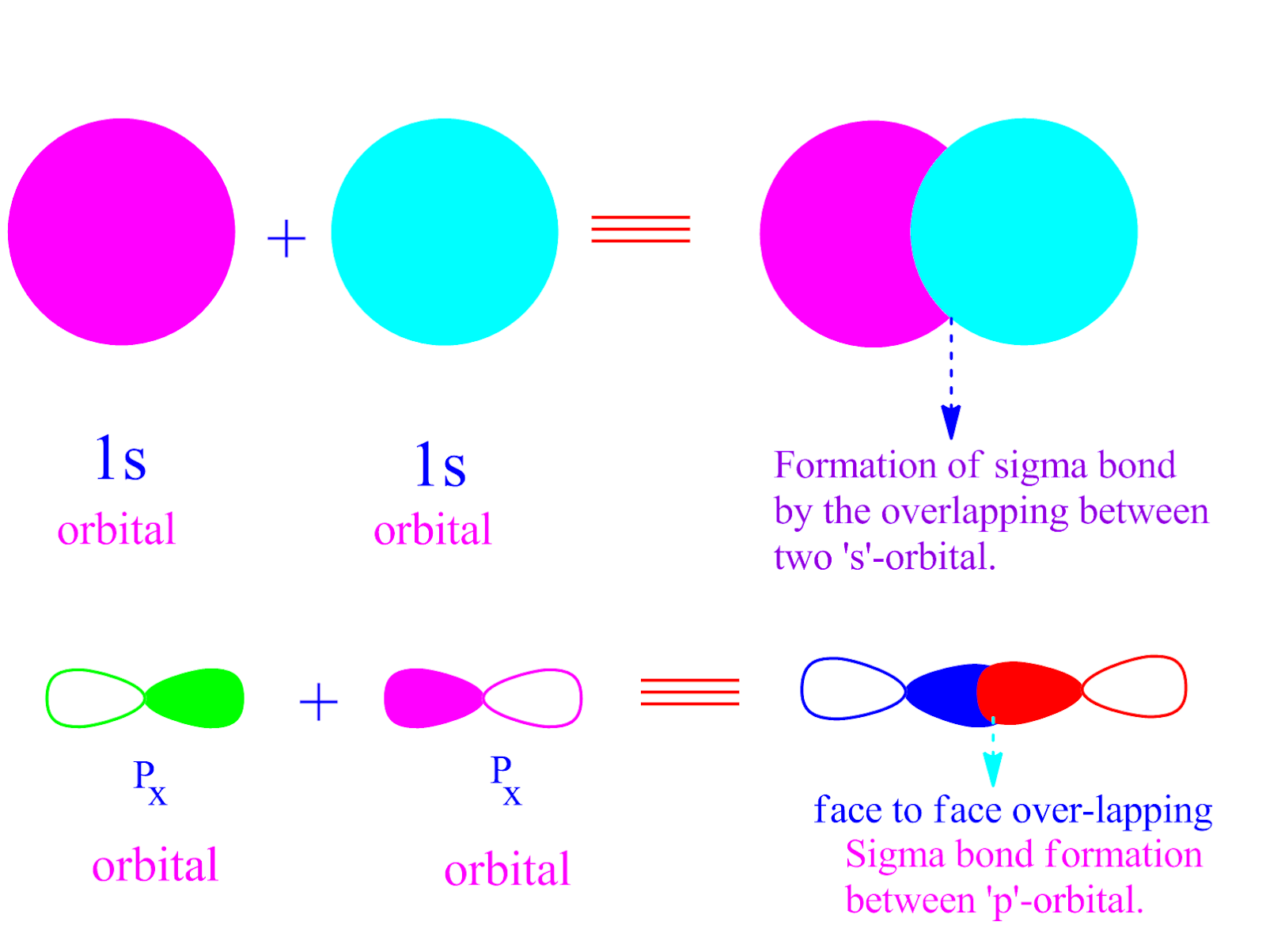
Unlike in double and triple bonds, atoms are free to rotate around a single bond. A sigma bond forms by head-on overlapping of σ orbitals. Usually, a single bond is a sigma bond, although the bond in diboron (B 2) is a pi bond. The notation for a single bond is a single dash between the atoms, such as H-H or Cl-Cl.Įxamples of single bonds are H 2 (hydrogen, H-H), F 2 (fluorine, F-F), some other diatomic molecules, hydrochloric acid (HCl, H-Cl), methane (CH 4), and NH 3 (ammonia). Atoms that form this type of bond are one electron away from a noble gas configuration, so elements participating in single bonds are hydrogen and the halogens, with each other or with other elements.

In other words, covalent bond formation is an exothermic process. Two atoms form a bond to increase their stability, which results in a loss of energy.According to Langmuir, covalence is the number of pairs of electrons shared between an atom and its neighbor. Irving Langmuir first described covalence in his 1919 article “The Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms and Molecules” in the Journal of the American Chemical Society. Note that sigma bond has been referred to as the strongest type of covalent bond because the extent of overlap is maximum in case of orbitals involved in the formation of the sigma bond. Here is a closer look at single, double, and triple bonds, along with examples of each type and their properties. Sigma bonds (\sigma) () are the strongest type of covalent bond, formed by head-on overlapping of atomic orbitals. Since metals usually need more than three electrons to achieve this, they less commonly form these types of bonds.
Atoms form these bonds as a way of obtaining the most stable electron configuration, according to the octet rule. Single, double, and triple bonds are three types of covalent bonds mainly involving nonmetals. This entry was posted on Jby Anne Helmenstine (updated on January 3, 2023)Ĭomparison of single, double, and triple bonds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
